AC2
F212 (hot-rolled)

Composition: Free machining steel. 0.10-0.14 C; 1.10-1.50 Mn; < 0.06 Si; < 0.11 P; <0.34-0.40 S; 0.20-0.35 Pb
Processing: Hot-rolled and air cooled.
Etching: 15-30s immersion in 2% nital.
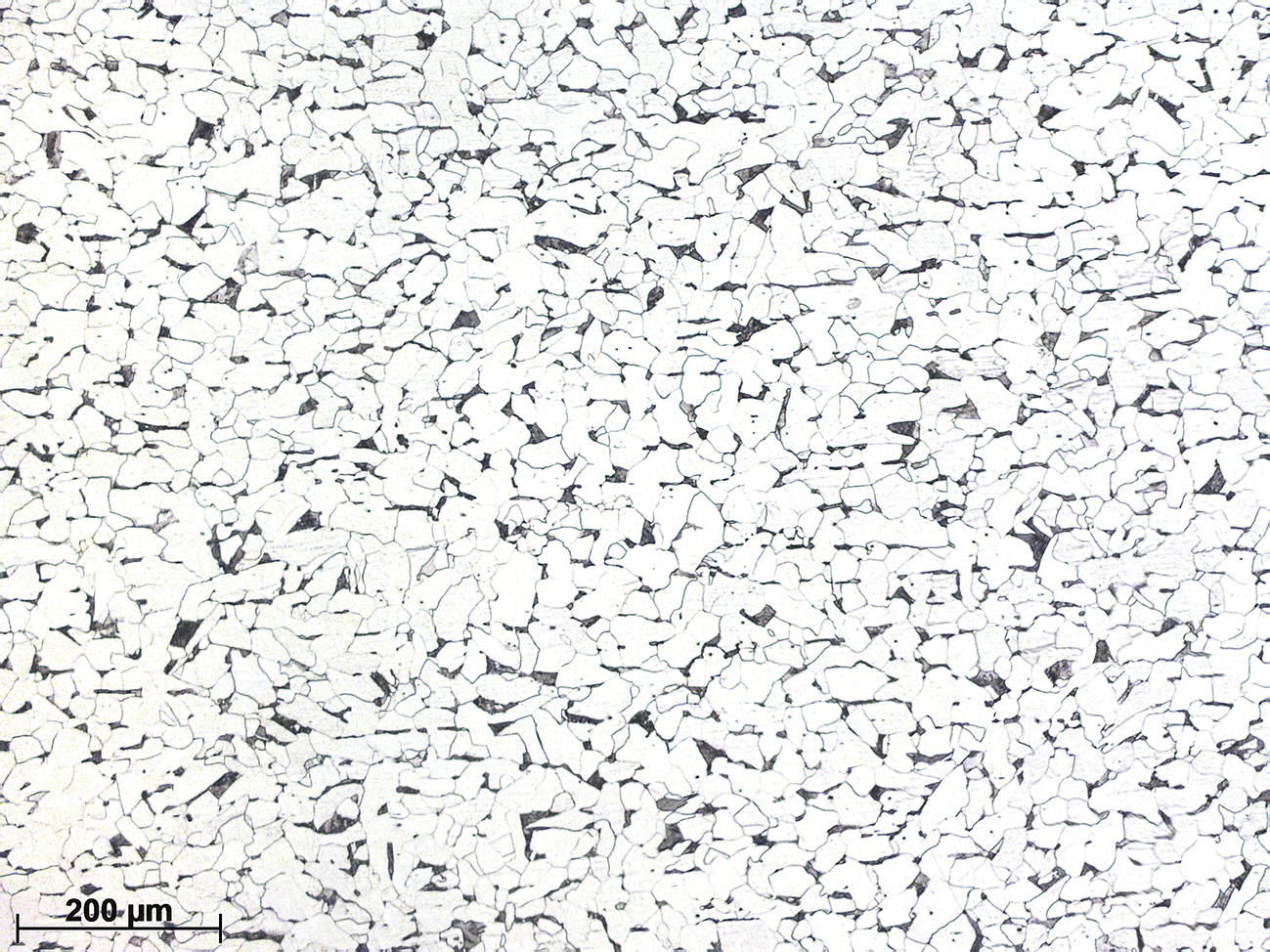
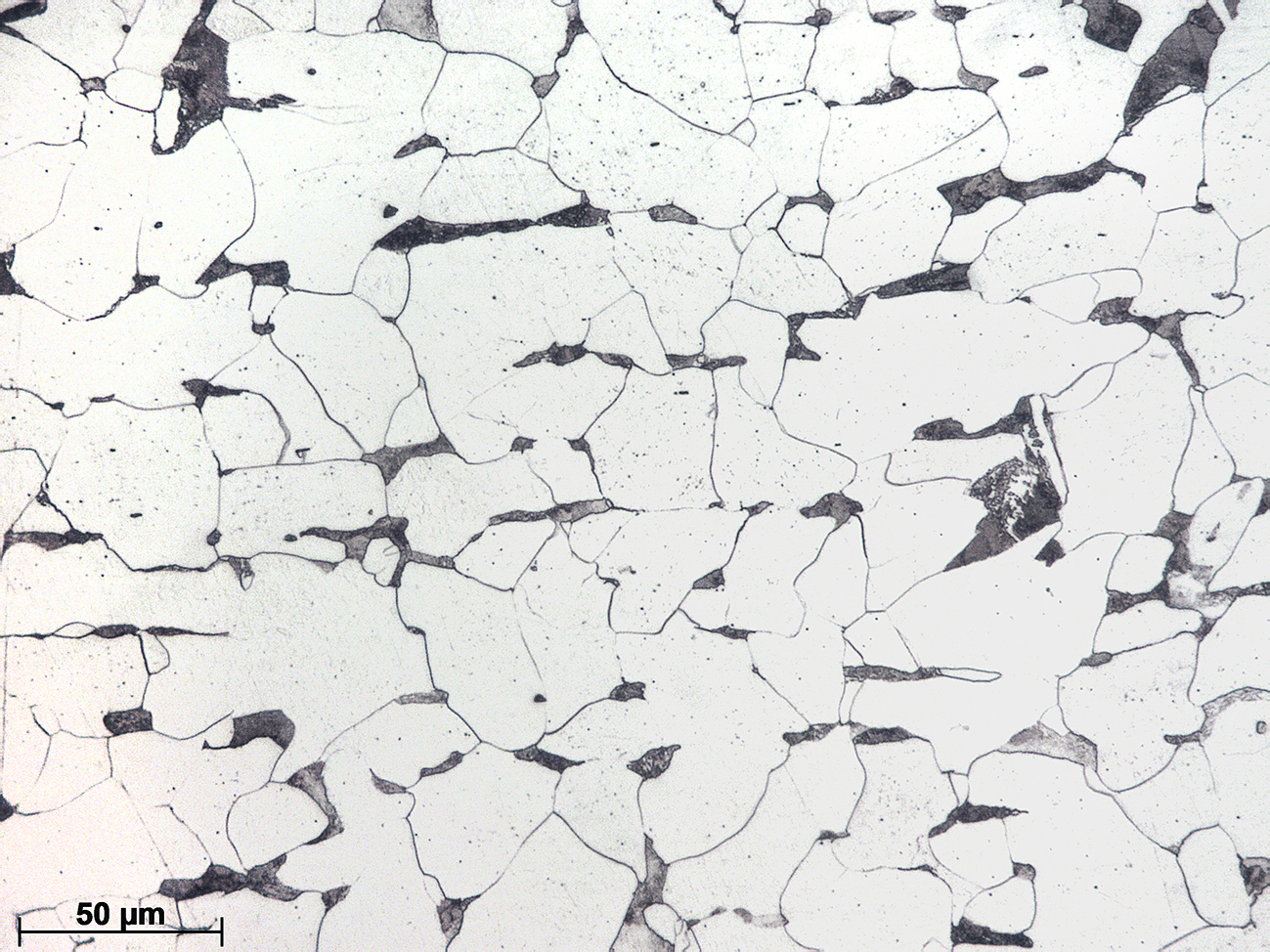
The micrographs show the characteristic microstructure of a hot-rolled steel consisting of ferrite (87%) and pearlite (13%). Elongated MnS inclusions, which are aligned with the rolling direction, and small globular lead particles are also visible.
This is a free machining steel high in sulphur with small Pb additions (< 0,35%). Conventional steels produce long and tangled chips during machining due to their high toughness. The addition of S promotes the formation of MnS inclusions that help fragmenting the chips, thus faciliting the machining process. An additional advantage of S is that the friccion coefficient is reduced, increaseing the tool life.
The presence of Pb also facilitates machining. The improvement is of the order of 20-30% in comparison with Pb-free steels. Pb is insoluble in steels at low temperatures and is dispersed as fine particles. These aid chip-breaking during machining and also serve as a lubricant.
Free machining steels can be surface hardened by processes such as carburization and carbonitriding followed by quenching and tempering.
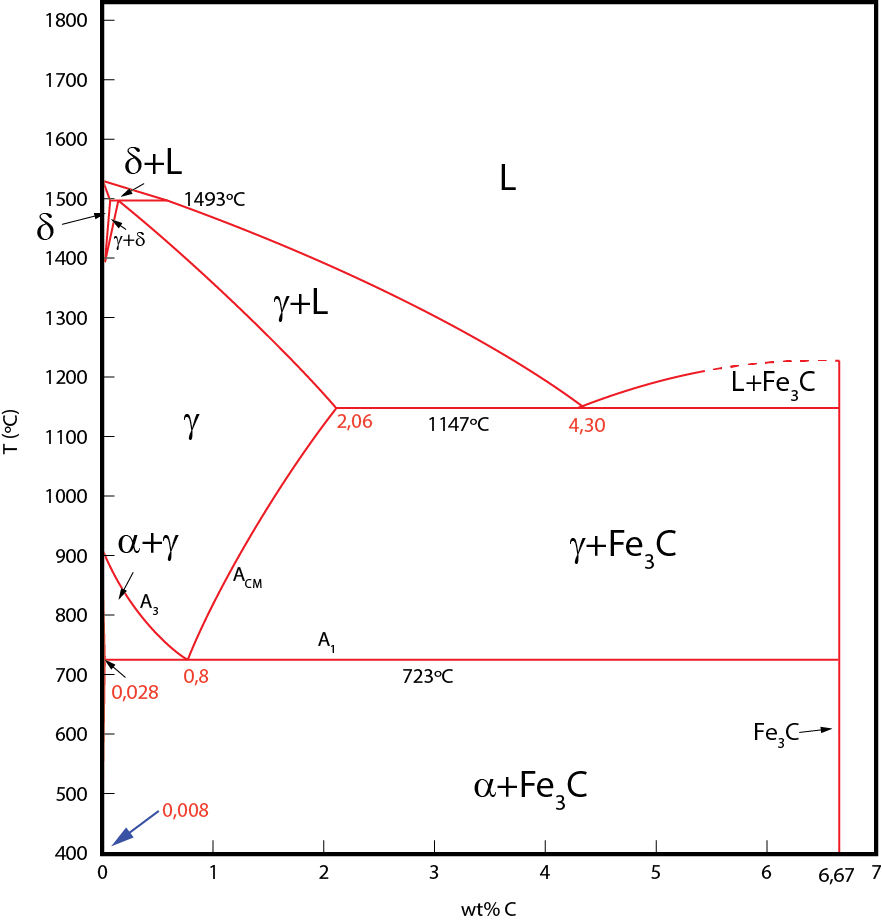
Fe-Fe3C diagram

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.