- Portada
- Líneas de investigación / Research lines
- Respuestas de adaptación a situaciones de estrés / Adaptive responses to cell wall stress
Respuestas de adaptación a situaciones de estrés / Adaptive responses to cell wall stress
Caracterización de respuestas de adaptación a situaciones de estrés sobre la pared celular
La pared celular fúngica es una estructura esencial, tanto para el mantenimiento de la morfología celular, como para la protección de la célula frente a las condiciones adversas del medio externo. Por ello, en situaciones de estrés que afectan a la integridad de esta estructura se induce, en S. cerevisiae, una respuesta de adaptación que tiene como consecuencia la reprogramación transcripcional de la célula, permitiendo a la célula sobrevivir en estas circunstancias.
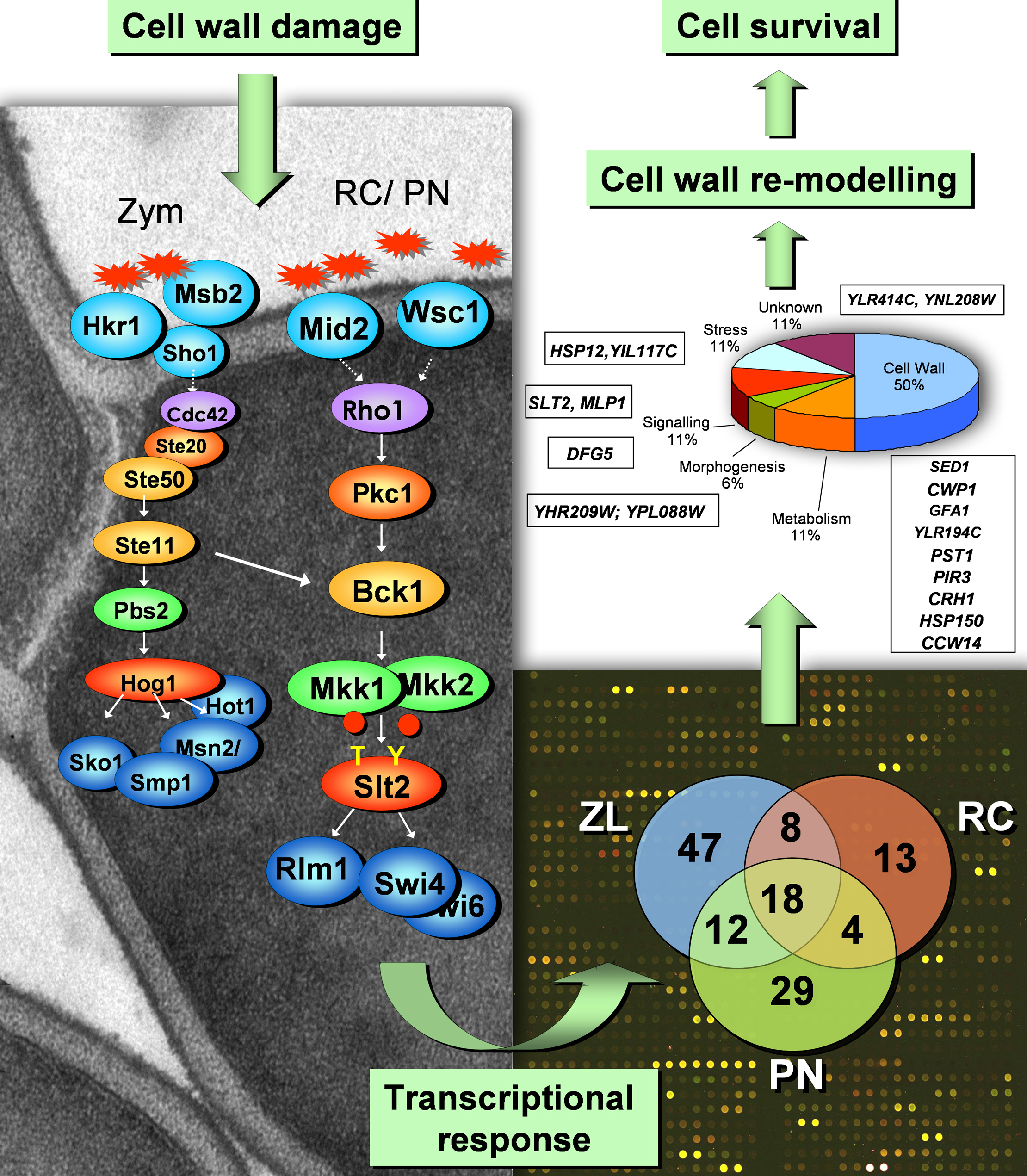
Nuestro laboratorio ha sido pionero en la caracterización de estas repuestas transcripcionales. La ruta de integridad celular o ruta CWI (Figura), mediada por la MAPK Slt2, a través del factor de transcripción Rlm1 y de distintos sensores dependiendo del tipo de daño, es la principal responsable de la de la activación de estas respuestas. Sin embargo, otras rutas de transducción de señales, como la ruta HOG y la ruta PKA también participan. Actualmente, nuestro principal interés se centra en la identificación y caracterización de nuevos elementos de regulación de estas respuestas celulares, a través de diversas aproximaciones genéticas y bioquímicas, así como mediante herramientas genómicas (desarrollo de screenings utilizando la colección completa de mutantes de S. cerevisiae) y proteómicas.
Characterization of adaptive responses to stress on the cell wall.
The fungal cell wall is an essential structure for the maintenance of cell morphology and to protect the cell against the adverse conditions of the external environment. Therefore, in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, under stressful situations affecting the integrity of this structure, an adaptive response is induced that results in the transcriptional reprogramming of the cell, allowing the cell to survive under these circumstances.
Our laboratory has pioneered the characterization of these transcriptional responses. The CWI route (Figure) through the Slt2 MAPK, the Rlm1 transcription factor and different sensors depending on the type of damage is the main responsible for the activation of these responses. However, other signal transduction pathways, such as HOG route and route PKA also participate. Currently, our main focus is on the identification and characterization of new regulatory elements of these cellular responses through genetic and biochemical approaches, as well as through genomics (development of screenings using the complete collection of mutants of S. cerevisiae) and proteomics tools.